What is Endpoint Security
Endpoint security is the process of safeguarding devices such as workstations, servers, and other systems capable of running security clients from malicious threats and cyberattacks. Endpoint security software allows businesses to protect devices used by employees for work, as well as servers on a network or in the cloud, from cyber threats.
The modern business landscape is experiencing a surge in cybersecurity threats from increasingly sophisticated cybercriminals. Hackers launch a cyberattack every 39 seconds, totaling 2,244 attacks per day. Endpoints are among the most common targets due to their vast number in use for network connections. Strategy Analytics insight reported 22 billion connected devices in 2018, with projections indicating this number will rise to 38.6 billion by 2025 and 50 billion by 2030. Consequently, Verizon’s threat report found that up to 30% of data breaches involved malware being installed on endpoints.
Every endpoint that connects to the corporate network represents a vulnerability, offering a potential entry point for cybercriminals. Thus, any device an employee uses to connect to business systems or resources carries the risk of becoming the conduit for a hacking attempt. These devices can be exploited by malware, which can leak or steal sensitive business data.
In response to these threats, it is imperative for businesses to deploy solutions that can analyze, detect, block, and contain cyberattacks in real-time. Organizations also need to collaborate with one another and utilize technologies that give their IT and security teams visibility into advanced threats, enabling the quick detection and swift remediation of potential security risks.
Why Is Endpoint Security Important?
Every device employees use to connect to business networks represents a potential risk that cybercriminals can exploit to steal corporate data. These devices, or endpoints, are proliferating, making the task of securing them increasingly difficult. Therefore, it is vital for businesses to deploy tools and solutions that protect their cybersecurity front line.
Benefits of An Endpoint Security
Endpoint security technology plays a crucial role in protecting organizations from the increasingly dangerous threat landscape. Some of the key benefits of an endpoint security approach include:
- Protecting all endpoints: As employees connect through an increasing number of endpoints and various types of devices, it is essential for organizations to ensure secure connections. This includes safeguarding the data on these devices to prevent loss or theft.
- Securing Remote Working: The rise in device usage corresponds with new work practices such as bring your own device (BYOD) and remote working policies. These policies allow employees to work effectively from anywhere on any device, but also introduce security vulnerabilities. An endpoint security platform is crucial for protecting these devices and ensuring secure work environments.
- Sophisticated Threat Protection: Hackers are using increasingly sophisticated methods to gain access to corporate networks, steal data, and manipulate employees into revealing sensitive information. Endpoint protection is essential for securing modern enterprises and preventing cybercriminals from infiltrating their networks.
- Protecting Identity: With employees accessing business systems from various devices, networks, and locations, traditional perimeter security is no longer sufficient. Endpoint security places protection directly on employees' devices, enabling safe work practices regardless of how and where they connect to corporate data and resources.
How Does Endpoint Security Work?
The main goal of any endpoint security solution is to protect the data and workflows associated with all devices that connect to the corporate network. It achieves this by examining files as they enter the network and comparing them against an ever-growing database of threat information stored in the cloud.
The endpoint security solution provides system administrators with a centralized management console, installed on a network or server, enabling them to control the security of all connected devices. Client software is deployed to each endpoint, either remotely or directly. Once the endpoint is set up, the software pushes updates as needed, authenticates login attempts, and administers corporate policies.
In addition, the endpoint security solution secures endpoints through application control. This blocks the user from downloading or accessing applications that are unsafe or unauthorized by the organization. It also uses encryption to prevent data loss.
The endpoint security solution enables businesses to quickly detect malware and other common security threats. Additionally, it provides endpoint monitoring, detection, and response capabilities, allowing the detection of more advanced threats such as fileless malware, polymorphic attacks, and zero-day attacks. This advanced approach offers enhanced visibility and a broader range of response options when facing a security threat.
What Is an Endpoint? - Endpoint Definition
An endpoint is any device that enables an employee to connect to a corporate network. With the growth of BYOD (bring your own device) policies and the proliferation of connected systems like the Internet of Things (IoT), the number of devices potentially connecting to a network is increasing exponentially.
Some of the more common devices that can be considered endpoints include:
- ATM machines
- IoT-enabled smart devices
- Industrial machines
- Laptop computers
- Medical devices
- Mobile phones
- Printers
- Servers
- Tablets
- Wearables, such as smartwatches
Endpoints now extend beyond the laptops and mobile phones that employees use to get their work done. They encompass any machine or connected device that could potentially connect to a corporate network. These endpoints are particularly lucrative entry points for hackers targeting business networks and systems. Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to consider every device connected to their network and ensure it is protected. Additionally, as endpoints evolve and become more sophisticated, so too must the security solutions that protect them from exploitation.
Endpoint Protection vs. Antivirus: What Is the Difference?
Antivirus software helps businesses detect, eliminate, and prevent malware from infecting devices. Installed directly on endpoint devices such as laptops, PCs, network servers, and mobile devices, antivirus solutions work by scanning files and directories to identify patterns matching known virus definitions and signatures. However, they can only recognize known threats and must be regularly updated to detect the latest malware strains.
Endpoint security threat prevention is fundamentally different from the approach of antivirus software. Instead of focusing on protecting individual devices, endpoint security solutions safeguard the entire business network, including all the endpoints connected to it.
Device Coverage:
- Antivirus Software: Designed to protect individual devices, such as laptops.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Aim to protect all connected devices across an entire enterprise network.
Protection from Threats:
- Antivirus Software: Protects against malware included in the database of known threats, potentially leaving businesses vulnerable to sophisticated, signatureless threats.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Offer holistic protection against various threats, including data loss, fileless malware, signatureless malware, and phishing attacks, in addition to known risks.
Continuous Protection:
- Antivirus Software: Uses signature-based detection, requiring manual updates to stay current, which can leave devices at risk if not updated.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Connect to the cloud and update automatically, ensuring users always have the latest protection.
Advanced Internal Protection:
- Antivirus Software: Can block malware but does not prevent employees from stealing data via USB drives.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Offer greater protection through data encryption and access controls, preventing unauthorized data access and theft. Advanced technologies like behavioral analysis detect threats based on suspicious behavior from both external and internal sources.
Admin Control:
- Antivirus Software: Relies on users to manually update the software to address new malware risks, introducing the risk of human error.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Shift the responsibility to the IT or security team, reducing human error and ensuring consistent protection.
Enterprise-Wide Control:
- Antivirus Software: Notifies users of threats, requiring in-person analysis and investigation by security professionals.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Provide a centralized portal for admins to monitor activity, install, configure, patch, update software, investigate suspicious traffic, and resolve issues remotely across multiple endpoints simultaneously, speeding up issue resolution and saving time for IT and security teams.
Integration:
- Antivirus Software: Operates as a single program with a specific function.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Offer integrated suites that combine various solutions for comprehensive security protection, enhancing overall security effectiveness.
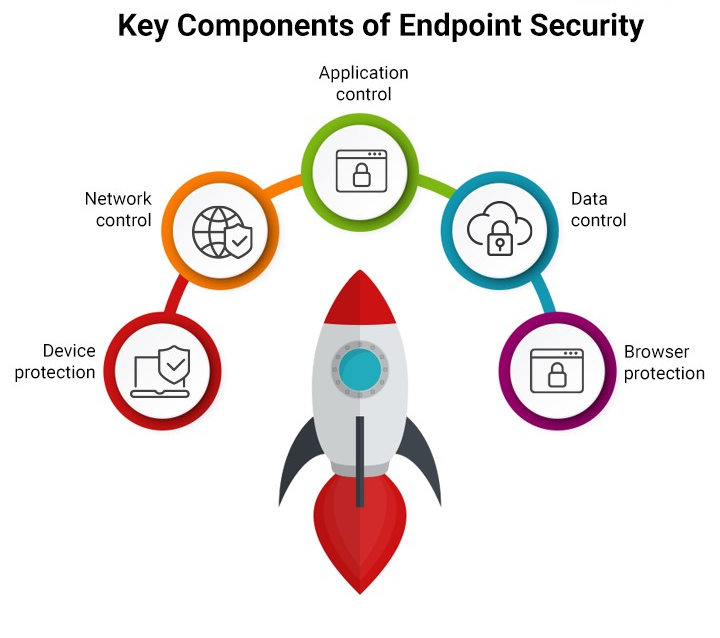
5 Key Components of Endpoint Security
A comprehensive endpoint security solution includes a centralized management console for monitoring and managing endpoints, real-time threat detection and response (EDR), antivirus and antimalware tools, and access to up-to-date threat intelligence. It protects data through encryption and data loss prevention (DLP), ensures only secure devices connect to the network via network access control (NAC), and regulates applications with application control. Patch management automates software updates, while strong user and device authentication verifies identities. An endpoint firewall monitors and controls network traffic, and behavioral analysis detects anomalies and potential threats.